Cas Enzymes for Advanced Genetic Engineering with CRISPR Technology
At Fortis Life Sciences, we bridge the gap by providing a comprehensive suite of application-specific Cas enzymes, coupled with stringent quality control measures. This rigorous approach ensures that our products consistently deliver the quality and performance researchers need to drive innovation across a range of fields, from molecular diagnostics to agricultural biotechnology.
CRISPR-Cas systems have emerged as powerful tools for genetic engineering, offering unprecedented precision in DNA and RNA targeting. These systems, derived from bacterial adaptive immune mechanisms, consist of a guide RNA (gRNA) that directs a Cas endonuclease to specific nucleic acid sequences for cleavage or modification. While CRISPR technology has opened new avenues in research and therapeutics, researchers often face challenges with enzyme stability, off-target effects, and the need for specialized Cas variants for different applications.
Key Benefits of Fortis Cas Enzymes
Precision and Efficiency
- Our Cas enzymes offer optimal target specificity, minimizing off-target effects, and are based on the wild-type (WT) versions of these enzymes
Versatility Across Applications
- Comprehensive range of Cas9, Cas12a, and Cas13a enzymes suitable for diverse research needs
- Each enzyme is optimized for its specific application, from genome editing to RNA targeting
Consistent, Reproducible Results
- cGMP compliant manufacturing in an ISO 13485 certified facility for batch-to-batch consistency
- Extensively purified and quality-controlled to ensure reproducibility in your experiments
Flexible Formulations
- Available in customizable concentrations and buffer compositions
- Options for lyophilized formats to enhance stability, consistency and ease of use
Our Cas Enzyme Portfolio
| Enzyme | Microbial Source | Co-RNA | Substrate | Collateral Nuclease Activity | Key features | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cas9 | Streptococcus pyogenes | crRNA + tracrRNA (or sgRNA) | dsDNA | No | Blunt-end cuts, widely used | Genome editing |
| Cas12a | Lachnospiraceae bacterium | crRNA | dsDNA, ssDNA | Yes | 5' overhang cuts, collateral ssDNase activity | Genome editing, Molecular diagnostics |
| Cas13a | Leptotrichia wadei | crRNA | RNA | Yes | RNA-targeting, collateral RNase activity | mRNA depletion, Molecular diagnostics |
All Fortis Cas enzymes are provided as a 10mg/mL stock solution in 50% glycerol storage buffer, with a C-terminal nuclear localization sequence for use in mammalian cells.
Cas9: The Cornerstone of Genome Editing
Applications:
Gene knockouts, insertions, precise modifications, and base editing in various organisms and cell types
Cas9 is the most widely used CRISPR endonuclease, known for its versatility in DNA editing applications. It creates blunt-end double-strand breaks at sites complementary to its guide RNA, requiring an NGG PAM sequence.
Custom Enzyme Development
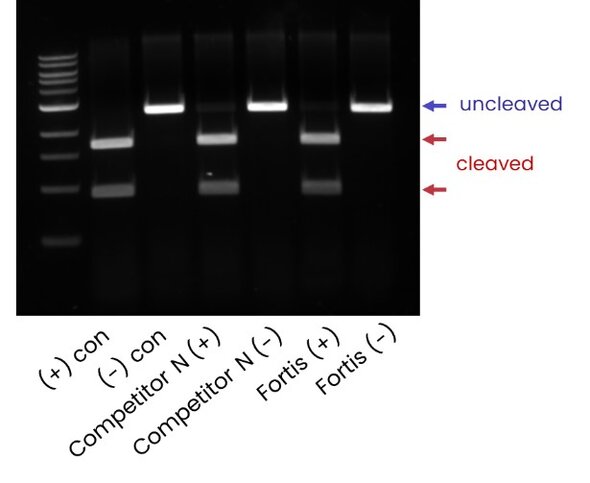
Figure 1: Fortis Cas9 on-target double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) cleavage: Gel electrophoresis shows the double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) cleavage activity of Fortis Cas9 and a leading competitor’s Cas9 against plasmid DNA substrate. Reactions were carried out with and without guide RNA (gRNA). Cleaved (red arrows) and uncleaved (blue arrows) DNA fragments indicate that Fortis Cas9 demonstrates similar cleavage efficiency to the competitor.
Cas12a (Cpf1): Precision Engineering for Specialized Needs
Applications:
Editing AT-rich genomic regions, homology-directed repair, and development of sensitive DNA detection assays for diagnostics
Cas12a offers unique advantages, including the generation of staggered DNA breaks with 5' overhangs and a preference for T-rich PAM sequences (TTTV). It also exhibits collateral single-stranded DNase activity when activated.
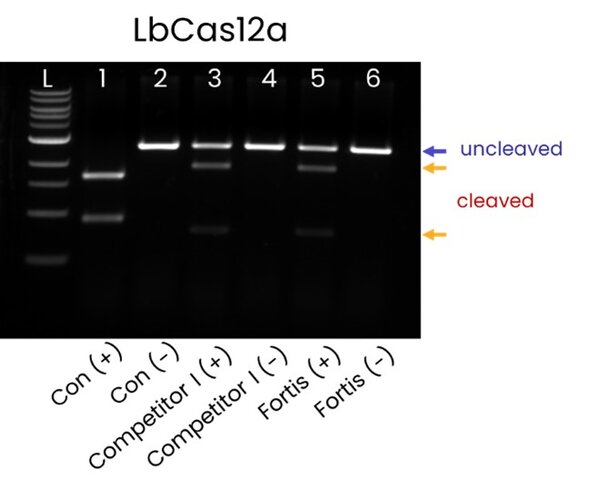
Figure 2: Fortis Cas12a on-target dsDNA cleavage activity: Gel electrophoresis comparing the dsDNA cleavage of Fortis Cas12a and a leading competitor plasmid DNA substrate. Cleaved (red arrows) and un-cleaved (blue arrows) bands indicate comparable cleavage efficiency between Fortis Cas12a and the competitor.
Cas13a: Expanding the CRISPR Toolkit to RNA
Applications:
Targeted RNA knockdown, study of RNA biology, and development of sensitive assays for RNA virus detection
Cas13a targets single-stranded RNA without requiring a PAM site, offering flexible guide RNA design. It exhibits collateral RNase activity upon target binding, making it a powerful tool for RNA biology and diagnostics.
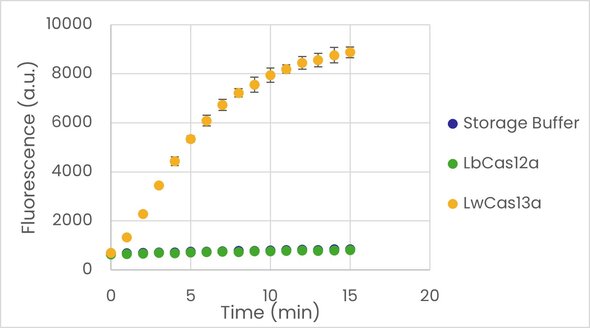
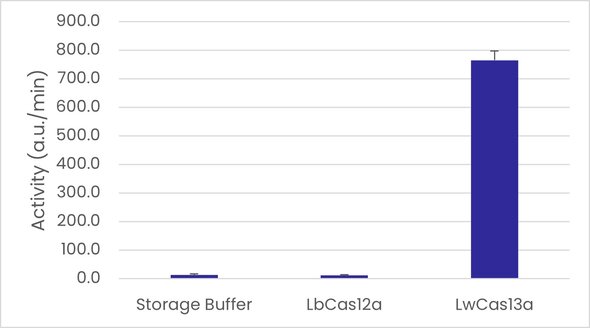
Figure 3: Fortis Cas13a enzyme displays reproducible target-activated collateral RNase activity: The left graph shows an increase in fluorescence over time, indicating RNA degradation. Fortis Cas13a demonstrates significantly higher RNase activity compared to LbCas12a and the control. The right graph quantifies RNase activity, confirming that Fortis Cas13a exhibits robust and reproducible RNA degradation.
Customization & Bulk Supply Options
Bulk Supply
For large-scale production initiatives and commercial applications, ensuring consistent quality and an uninterrupted supply chain for your critical processes
Lyophilization Services
To enhance product stability, extend shelf life, and simplify storage and transportation for global distribution networks
Custom Services
For enzyme concentrations and buffer formulations to align precisely with your manufacturing processes and end-product specifications, maximizing efficiency and performance
